Past Perfect Tense | Examples & Exercises
The past perfect tense is a verb form used to refer to a past action that occurred before another past action.
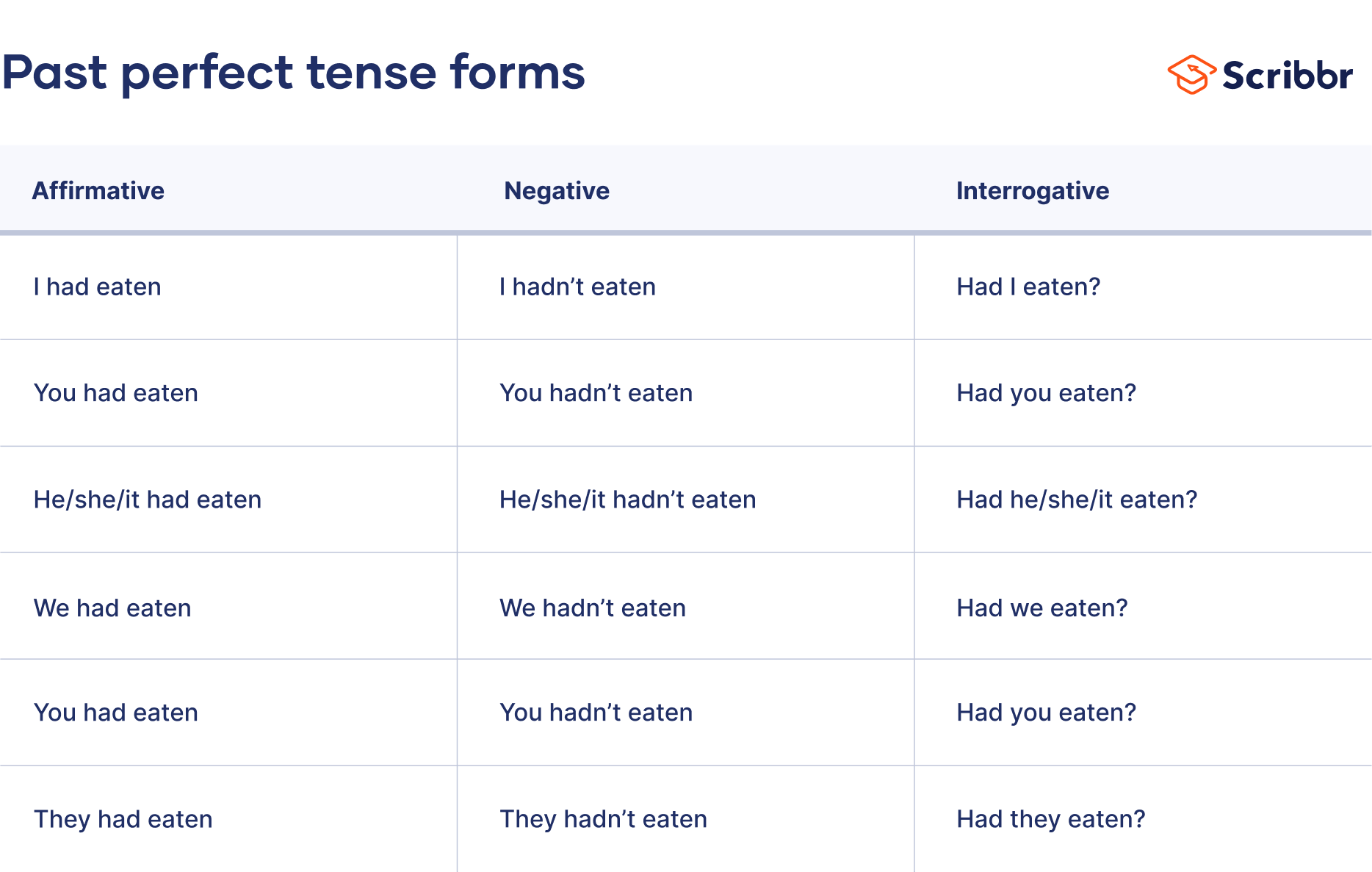
The past perfect is formed using “had” along with the past participle of the main verb (e.g., “I had run”). All verbs in the past perfect tense take this form regardless of the subject (e.g., “she had known,” ”we had known”).
How to use the past perfect
The past perfect tense (also called the pluperfect) is used:
- to describe a past event that occurred prior to another past event
- to talk about time up to a certain point in the past
- in conditional sentences to talk about an unreal past event and its hypothetical consequence
The past perfect is formed using the auxiliary verb “had” along with a past participle.
When I got home, I realized I had left my keys at the office.
Nobody noticed that the chef had burned the turkey.
If you had asked me, I would have picked you up.
Present perfect vs. past perfect
While both the present perfect and past perfect tenses are used to refer to past actions and events, they serve different purposes:
- The present perfect is used to describe a past action that has present consequences or an action that began in the past and may continue.
- The past perfect is used to describe a past action that occurred before another action (in the past simple tense).
I had eaten at that restaurant many times before it closed.
Pritha has read the book and is excited about the film.
Pritha had read the book before she watched the film adaptation.
Simple past vs. past perfect
Both the simple past tense and past perfect tense are used to describe past action or events. However, they have different functions:
- The past simple is used to indicate that an action or series of actions were completed in the past.
- The past perfect is used to indicate that an action occurred before another past action. Sentences that use the past perfect often have a clause in the simple past to indicate that one past action occurred before another.
Andrew had worked at the company for five years before he quit.
How to form negatives
In the past perfect tense, negative statements are formed by adding the adverb “not” after the auxiliary verb “had.” This is often contracted (i.e., “hadn’t”).
By the end of the meeting, they still hadn’t decided on a plan.
I ordered takeout last night because I hadn’t bought groceries.
How to form questions
To ask a yes–no question using the past perfect, put the auxiliary verb “had” before the subject of the sentence and the past participle of the main verb.
Had you met Peter before last night?
To ask a question with a wh-word (an interrogative adverb like “when” or interrogative pronoun like “what”), follow the same order as above and add the adverb or pronoun at the beginning of the sentence.
Who had you invited to the party before it was canceled?
Exercises: Past perfect tense
Practice using the past perfect correctly with the exercises below. In the blank space in each sentence, fill in the correct past perfect form based on the subject and verb specified (e.g., “[I / see]” becomes “I had seen”). Some answers may also be negative statements or questions.
- __________ [The thieves / expect] to find the diamonds in the vault.
- They went to watch a movie after __________ [they / finish] their homework.
- __________ [John / not / sleep] well, and he could not focus.
- What __________ [Aaron / study] before he became a writer?
- The thieves had expected to find the diamonds in the vault.
- The past perfect is formed using “had” and the past participle of the main verb.
- They went to watch a movie after they had finished their homework.
- The past perfect is used to describe a past action that was completed before another past action occurred.
- John had not slept well, and he could not focus.
- Negative statements are formed by adding “not” after the auxiliary verb “had.”
- What had Aaron studied before he became a writer?
- To ask a question with a wh-word, add the question word at the beginning of the sentence, followed by the auxiliary verb “had,” the subject of the sentence, and the past participle of the main verb.
Other interesting articles
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or writing rules make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Academic Writing
AI
Frequently asked questions about the past perfect tense
- What is the past perfect continuous?
-
The past perfect continuous is a verb form used to refer to an action that began in the past and continued up until another time in the past.
The past perfect continuous is formed using the auxiliary verbs “had” and “been,” along with the present participle of the main verb (e.g., “I had been working”).
The past perfect continuous is one of four past tense verb forms, along with the simple past, past progressive, and past perfect tense.
- What is the past perfect form of “go”?
-
The past perfect tense is a verb form used to describe a past action that occurred before another past action.
The past perfect is formed using the auxiliary verb “had” and the past participle of the main verb.
The past perfect form of “go” is “had gone” (e.g., “I had gone”).
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, November 01). Past Perfect Tense | Examples & Exercises. Scribbr. Retrieved April 28, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/verbs/past-perfect/