Can you use Turnitin for free?
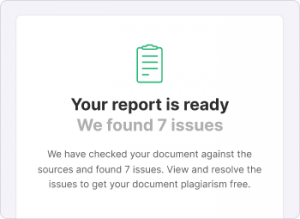
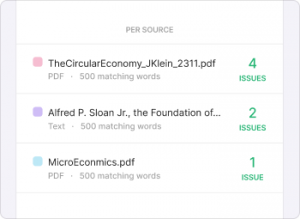
Yes, Scribbr offers a limited free version of its plagiarism checker in partnership with Turnitin. It uses Turnitin’s industry-leading plagiarism detection technology and has access to most content databases.
If you’re a university representative, you can contact the sales department of Turnitin.